本文参考自:Polymorphism in C++
多态,简单来说,我们可以将多态性定义为消息以多种形式显示的能力。举例来说:比如一个人同时可以有多种性格特征。像一个男人他可能是一个父亲,一个丈夫,或是一个公司雇员。所以同一个人在不同的情况下会有不同的行为。这称为多态性。多态性被认为是面向对象编程的重要特征之一。
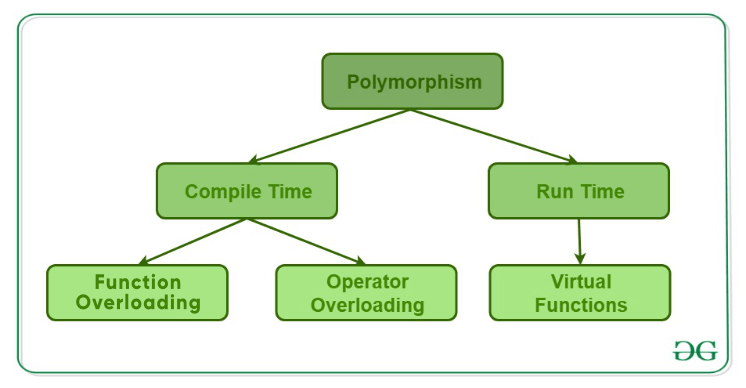
C++多态一般分为两种类型:编译时多态和运行时多态。
Compile time polymorphism 编译时多态
编译时多态,这种类型的多态性是通过函数重载(function overloading)或运算符重载(operator overloading)来实现的。
Function Overloading 函数重载
当两个或多个函数同名但具有不同参数称为函数重载。函数可以通过更改参数数量或更改参数类型来重载。
Rules of Function Overloading
// C++ program for function overloading
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Geeks
{
public:
// function with 1 int parameter
void func(int x)
{
cout << "value of x is " << x << endl;
}
// function with same name but 1 double parameter
void func(double x)
{
cout << "value of x is " << x << endl;
}
// function with same name and 2 int parameters
void func(int x, int y)
{
cout << "value of x and y is " << x << ", " << y << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Geeks obj1;
// Which function is called will depend on the parameters passed
// The first 'func' is called
obj1.func(7);
// The second 'func' is called
obj1.func(9.132);
// The third 'func' is called
obj1.func(85, 64);
return 0;
}
Output:
value of x is 7
value of x is 9.132
value of x and y is 85, 64
Operator OverLoading 运算符重载
C++还提供了重载运算符的操作。例如,我们可以为string类实现(’+’)运算符来连接两个字符串。我们已知这是将两个操作数相加的加法运算符。因此,单目运算符(’+’)放在整形操作数之间时,执行相加操作;而当其放置在字符串操作数之间时,执行字符串连接操作。
Example:
// CPP program to illustrate
// Operator Overloading
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex
{
private:
int real, imag;
public:
Complex(int r = 0, int i = 0)
{
real = r;
imag = i;
}
// This is automatically called when '+' is used with
// between two Complex objects
Complex operator+(Complex const &obj)
{
Complex res;
res.real = real + obj.real;
res.imag = imag + obj.imag;
return res;
}
void print() { cout << real << " + i" << imag << endl; }
};
int main()
{
Complex c1(10, 5), c2(2, 4);
Complex c3 = c1 + c2; // An example call to "operator+"
c3.print();
}
Output:
12 + i9
上例中,运算符(’+’)被重载了。运算符(’+’)是一个加法运算符,可以将两个数字(整数或浮点数)相加,但这里的运算符用于执行两个虚数或复数的加法。要详细了解运算符重载,请访问此链接。
Runtime polymorphism 运行时多态
运行时多态也是通过函数重载实现的。
Function overriding
当派生类具有基类的一个成员函数的定义时,就会发生函数重载。此时,可以说基函数被重载了(overridden)。
// C++ program for function overriding
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class base
{
public:
virtual void print()
{
cout << "print base class" << endl;
}
void show()
{
cout << "show base class" << endl;
}
};
class derived : public base
{
public:
void print() // print () is already virtual function in derived class, we could also declared as virtual void print () explicitly
{
cout << "print derived class" << endl;
}
void show()
{
cout << "show derived class" << endl;
}
};
// main function
int main()
{
base *bptr;
derived d;
bptr = &d;
// virtual function, binded at runtime (Runtime polymorphism)
bptr->print();
// Non-virtual function, binded at compile time
bptr->show();
return 0;
}
Output:
print derived class
show base class
要详细了解运行时多态性,请访问此链接。
「如果这篇文章对你有用,请随意打赏」
如果这篇文章对你有用,请随意打赏
使用微信扫描二维码完成支付

comments powered by Disqus